How to Become a Nurse Anesthetist?
How to Become a Nurse Anesthetist?
Becoming a nurse anesthetist is a journey that brings together a passion for patient care, a commitment to excellence, and a deep understanding of medical science. Nurse anesthetists are advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) who play a vital role in the healthcare system by administering anesthesia to patients undergoing surgical procedures. Their expertise in anesthesia management ensures that patients receive safe and effective pain relief during medical interventions.
Becoming a nurse anesthetist is challenging and rewarding, requiring a significant investment of time and dedication. This comprehensive guide will outline the steps, educational requirements, and essential skills necessary to embark on this fulfilling career. From obtaining a Bachelor’s degree in nursing to gaining specialized training and certification, we will explore each phase of the journey and shed light on nurse anesthetists’ critical role in modern healthcare.

If you aspire to work at the forefront of patient care, make a difference in people’s lives, and contribute to the advancement of medical science, joining the ranks of nurse anesthetists may be the path for you. Let’s delve into anesthesia and discover how to become a nurse anesthetist.
Educational Requirements for a Nurse Anesthetist
To become a nurse anesthetist, individuals must meet specific educational requirements, which include obtaining a Bachelor’s degree in nursing, gaining clinical experience as a registered nurse (RN), and pursuing a Master’s degree in nurse anesthesia. This section will delve into each of these educational steps in detail:
1. Bachelor’s Degree in Nursing (BSN)
The first step to becoming a nurse anesthetist is to earn a Bachelor’s degree in nursing. This typically involves a four-year undergraduate program offered by accredited colleges or universities. Aspiring nurses acquire a strong foundation in nursing theory, health sciences, and practical clinical experiences during the BSN program. Coursework may cover anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, microbiology, and patient care.
2. Clinical Experience as a Registered Nurse (RN)
After completing the BSN program, individuals must become licensed registered nurses (RNs) by passing the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). Once licensed, RNs gain invaluable clinical experience by working in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, or community health centers. It is essential to accrue at least one year of full-time, hands-on nursing experience before progressing to the next step.
3. Master’s Degree in Nurse Anesthesia (MSN or DNP)
The most critical educational requirement for becoming a nurse anesthetist is obtaining a Master’s degree in nurse anesthesia. Some programs offer a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) associate degree specializing in nurse anesthesia. Accredited nurse anesthesia schools or universities typically offer these specialized programs.
Nurse anesthesia programs are highly competitive and demanding. The curriculum includes in-depth studies on anesthesia principles, advanced pharmacology, physiology, pathophysiology, and techniques. Students also participate in supervised clinical rotations, where they gain practical experience administering anesthesia to patients undergoing various surgical procedures.
The duration of nurse anesthesia programs varies, but it usually takes 24 to 36 months to complete. Upon completing the program, graduates can take the national certification examination.
4. Certification and Licensure
After completing the nurse anesthesia program, aspiring nurse anesthetists must pass the National Certification Examination (NCE) administered by the National Board of Certification and Recertification for Nurse Anesthetists (NBCRNA). Successfully passing this exam leads to the official credential of Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA).
Additionally, to practice as a nurse anesthetist, individuals must obtain licensure as an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) in their respective state. Licensure requirements vary by state but typically involve fulfilling educational and certification criteria, along with passing a state-specific licensing exam.
Continuing Education
Nurse anesthetists must continue their education to maintain their certification and licensure. This ensures they stay current with the latest advancements in anesthesia techniques, medical practices, and patient care.
By meeting these educational requirements, aspiring nurse anesthetists can pave the way to a fulfilling and challenging career in healthcare. With their advanced skills in anesthesia management, nurse anesthetists play a crucial role in ensuring patient comfort and safety during surgical procedures.
Clinical Experience and Training
Clinical experience and training are integral components of the journey to becoming a nurse anesthetist. This phase allows aspiring nurse anesthetists to apply their theoretical knowledge in real-world settings, develop critical skills, and gain hands-on experience in administering anesthesia. This section will explore the key aspects of clinical experience and training for nurse anesthetists:

Nurse Anesthesia Clinical Rotations
During their Master’s or Doctoral program in nurse anesthesia, students must complete a series of clinical rotations. These rotations occur in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, surgical centers, and specialty clinics. Clinical rotations allow students to work with diverse patient populations and experience different surgical procedures.
Under the guidance and supervision of experienced nurse anesthetists and anesthesiologists, students observe and actively participate in anesthesia care. They learn to assess patients’ health status, devise anesthesia plans, administer anesthesia medications, and manage patients’ vital signs throughout surgical procedures.
Hands-on Experience with Anesthesia Techniques
Nurse anesthesia students are exposed to a wide range of anesthesia techniques throughout their clinical training. These may include general, regional, local, and monitored anesthesia care (MAC). Each technique requires specific skills and understanding, and students gain proficiency in tailoring anesthesia plans to meet individual patient needs.
As they progress through their clinical rotations, students are assigned increasing levels of responsibility, gradually taking on more complex cases under supervision. This hands-on experience prepares them for the challenges they will encounter in their future career as nurse anesthetists.
Preparing for Certification Examinations
Nurse anesthesia students must also begin preparing for their certification examinations during clinical training. The National Board of Certification and Recertification for Nurse Anesthetists (NBCRNA) administers the National Certification Examination (NCE) for nurse anesthetists. This comprehensive exam assesses the student’s knowledge, clinical judgment, and anesthesia management skills.
As the completion of the nurse anesthesia program nears, students typically devote time to review and comprehensive preparation for the NCE. Success in this examination is crucial as it leads to official certification as a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA).
Clinical experience and training are vital aspects of the educational journey for nurse anesthetists. The exposure to diverse clinical scenarios, combined with rigorous hands-on practice, equips future nurse anesthetists with the skills and confidence needed to provide safe and effective anesthesia care to patients undergoing various surgical procedures.
Licensure and Certification for Nurse Anesthetist
Licensure and certification are crucial steps for nurse anesthetists to practice legally and demonstrate their competency in the field. These processes involve obtaining state licensure as an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) and achieving national certification as a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA). Let’s explore the licensure and certification requirements for nurse anesthetists:
Obtaining RN Licensure
Before pursuing a career as a nurse anesthetist, individuals must first become licensed registered nurses (RNs). Aspiring nurses must pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN) to obtain RN licensure. This standardized exam assesses the knowledge and skills necessary for safe and competent nursing practice.
RN licensure requirements may vary slightly from state to state, so candidates need to review the state’s specific requirements where they intend to practice as an RN.
Applying for Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) Licensure
After completing the Master’s or Doctoral degree in nurse anesthesia, nurse anesthetists are eligible to apply for APRN licensure. APRN licensure allows nurse anesthetists to practice as advanced practice nurses, providing specialized anesthesia care to patients.
APRN licensure requirements also vary by state, but common prerequisites include:
- Completion of an accredited nurse anesthesia program.
- National certification as a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA).
- Submission of the required documentation, including transcripts, certification details, and proof of clinical experience.
- Payment of application and licensing fees.
Overview of Certification Bodies
To become a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA), nurse anesthetists must pass the National Certification Examination (NCE), which is administered by the National Board of Certification and Recertification for Nurse Anesthetists (NBCRNA). The NCE assesses the nurse anesthetist’s knowledge, skills, and ability to provide safe anesthesia care to patients.
The certification process involves meeting specific eligibility criteria, submitting an application, and scheduling the examination. Successful completion of the NCE leads to official certification as a CRNA, a significant milestone in the nurse anesthetist’s career.
It is important to note that nurse anesthetists must maintain their certification through ongoing professional development and recertification requirements set by the NBCRNA.
Licensure and certification are essential for nurse anesthetists to demonstrate their competence and commitment to providing high-quality anesthesia care. By meeting these requirements, nurse anesthetists can practice legally and gain the trust of patients, healthcare professionals, and healthcare institutions alike.
Skills and Qualities of a Successful Nurse Anesthetist
Becoming a successful nurse anesthetist goes beyond completing the necessary education and training. It requires unique skills and qualities that enable nurse anesthetists to provide safe and effective anesthesia care to patients while working in a high-stress environment. Here are some of the key skills and qualities of a successful nurse anesthetist:
1. Strong Medical Knowledge and Technical Skills
Nurse anesthetists must comprehensively understand anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and pathophysiology. They need to be well-versed in various anesthesia techniques and have the technical proficiency to administer anesthesia safely and accurately. Continuous learning and staying updated with the latest medical advancements are essential to providing the best possible care to patients.
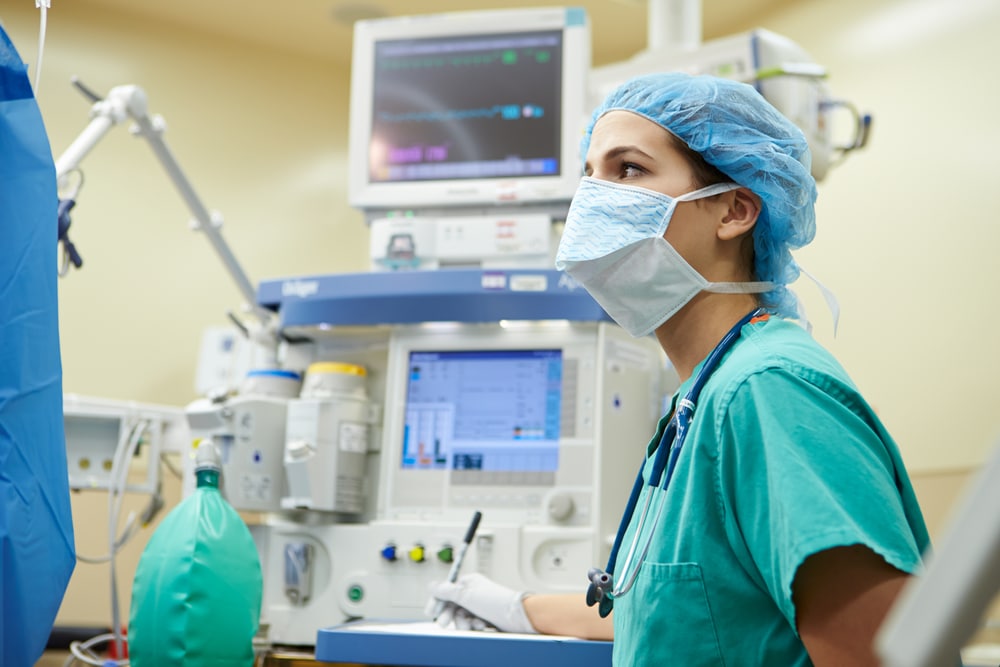
2. Attention to Detail and Critical Thinking
Anesthesia administration requires precise calculations and attention to detail. Nurse anesthetists must be meticulous in their assessments, planning, and monitoring during surgical procedures. They must also possess strong critical thinking skills to make quick and informed decisions in emergency situations or when unexpected complications arise.
3. Effective Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Nurse anesthetists work as part of a multidisciplinary healthcare team, which includes surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and other medical professionals. Effective communication and teamwork are crucial to ensure coordinated care and patient safety. Moreover, nurse anesthetists must be skilled in communicating complex medical information clearly and understandably to patients and their families.
4. Ability to Handle High-Stress Situations
The operating room can be a high-stress environment, especially during emergency surgeries. Nurse anesthetists must remain calm under pressure and exhibit emotional resilience. Managing stress and maintaining composure during challenging situations is vital to delivering quality care and ensuring patient well-being.
5. Compassion and Empathy for Patients
Nurse anesthetists work closely with patients who may be anxious or scared about their surgical procedures. Demonstrating compassion, empathy, and a caring attitude can help ease patients’ fears and create a positive patient experience. Building a trusting relationship with patients fosters better communication and cooperation during anesthesia.
6. Strong Ethical Standards and Professionalism
Nurse anesthetists must adhere to the highest ethical standards, maintaining patient confidentiality and upholding professional integrity. They are responsible for advocating for patient safety and autonomy while adhering to the principles of evidence-based practice.
7. Adaptability and Flexibility
Each surgical case may present unique challenges, and the healthcare landscape constantly evolves. Nurse anesthetists must be adaptable and flexible in their approach to care, adjusting their plans and techniques based on individual patient needs and changing circumstances.
8. Continuous Learning and Professional Development
Successful nurse anesthetists are committed to lifelong learning and professional development. They actively seek opportunities to enhance their knowledge, skills, and expertise through attending conferences and workshops or pursuing additional certifications or advanced degrees.
Nurse Anesthetist Job Outlook and Salary
The job outlook for nurse anesthetists is generally favorable due to the increasing demand for advanced practice nurses and their essential role in healthcare. As highly skilled anesthesia providers, nurse anesthetists are in high demand in various healthcare settings. Additionally, the complexity of surgical procedures and the need for specialized anesthesia care continue to drive the demand for their services. Here’s an overview of the job outlook and salary prospects for nurse anesthetists:
Job Outlook
The demand for nurse anesthetists is expected to grow at a faster rate than many other occupations in the healthcare industry. Factors contributing to this positive job outlook include:
- Aging Population: As the population ages, the need for surgical interventions and medical procedures is increasing. Elderly individuals often require surgical care, leading to a rise in demand for anesthesia services.
- Advancements in Medical Technology: Advancements in medical technology have enabled more complex and specialized surgeries to be performed. Nurse anesthetists’ expertise in anesthesia management is essential in ensuring the safety and well-being of patients during these procedures.
- Shortage of Anesthesiologists: In some regions, there is a shortage of anesthesiologists, leading to an increased reliance on nurse anesthetists to fill the gap in anesthesia care provision.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Healthcare institutions recognize the cost-effectiveness of employing nurse anesthetists, as they can provide high-quality anesthesia care with similar outcomes to anesthesiologists at a lower cost.
Salary
Nurse anesthetists are among the highest-paid nursing professionals, reflecting the level of skill and responsibility required for their role. The salary for nurse anesthetists can vary depending on factors such as geographic location, years of experience, and the employing institution. Generally, nurse anesthetists can expect competitive and lucrative salaries.
The median annual wage for nurse anesthetists in the United States was around $189,190, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). However, it is essential to note that salaries may have changed since then due to various economic factors and regional variations.
Keep in mind that salary figures can fluctuate, so it is recommended to refer to up-to-date sources such as the BLS or professional organizations like the American Association of Nurse Anesthetists (AANA) for the most current salary data.
Challenges and Rewards of Being a Nurse Anesthetist
Being a nurse anesthetist comes with a unique set of challenges and rewards. As highly skilled and specialized healthcare professionals, nurse anesthetists play a crucial role in patient care during surgical procedures. However, they also face various challenges in their day-to-day work. Let’s explore the challenges and rewards of being a nurse anesthetist:

Challenges
- High Responsibility and Pressure: Nurse anesthetists administer anesthesia and ensure patient safety during surgeries. The weight of this responsibility can be immense, especially during complex or high-risk procedures, leading to significant pressure on the nurse anesthetist.
- Long and Irregular Hours: Nurse anesthetists may work long hours and be on call during evenings, weekends, and holidays. Surgical procedures often occur at any time of the day or night, requiring nurse anesthetists to be available whenever needed.
- High-Stress Environment: The operating room is a high-stress environment where split-second decisions can significantly impact patient outcomes. Nurse anesthetists must remain composed under pressure and be prepared to handle emergencies or unexpected complications.
- Continuous Learning and Keeping Updated: Medical advancements and new anesthesia techniques are constantly evolving. Nurse anesthetists must engage in ongoing education and professional development to stay current with the latest practices and technology.
- Emotional Toll: Witnessing patients in distress or experiencing medical complications can emotionally impact nurse anesthetists. Providing compassionate care while maintaining professional detachment can be challenging.
Rewards
- Making a Difference in Patients’ Lives: Nurse anesthetists directly impact patients’ surgical experiences, ensuring they receive safe and effective anesthesia care. Being a part of the patient’s journey to improved health can be highly rewarding.
- High Level of Autonomy: Nurse anesthetists often work independently and make critical decisions about anesthesia care. This level of autonomy allows them to take ownership of their practice and contribute significantly to patient outcomes.
- Job Satisfaction: Nurse anesthetists often report high job satisfaction due to the level of expertise they bring to patient care, the challenges they overcome, and the positive outcomes they achieve.
- Competitive Salary: As advanced practice nurses, nurse anesthetists are among the highest-paid nursing professionals. The attractive salary is a rewarding aspect of their career.
- Versatile Career Opportunities: Nurse anesthetists can work in a variety of settings, including hospitals, surgical centers, clinics, and the military. The versatility of their skills allows for diverse career opportunities.
- Continuous Learning and Advancement: The dynamic nature of anesthesia care offers nurse anesthetists continuous learning opportunities. They can also pursue advanced degrees or specialize in specific areas of anesthesia care, further advancing their careers.
Future Trends in Nurse Anesthesia
The future of nurse anesthesia promises exciting advancements and opportunities. Technological innovations will likely enhance anesthesia delivery with improved monitoring systems, precision dosing, and advanced anesthesia techniques. Collaborative care models will become more prevalent, fostering stronger partnerships between nurse anesthetists and healthcare professionals. Nurse anesthetists will continue to advocate for patient safety and contribute to healthcare policy development.
Expanding telehealth and remote anesthesia monitoring may offer new ways for nurse anesthetists to provide care in diverse settings. As the demand for surgical interventions and anesthesia services grows, nurse anesthetists will remain at the forefront of healthcare, contributing to improved patient outcomes and promoting excellence in anesthesia care.
Final Thoughts
Becoming a nurse anesthetist is a journey that demands dedication, passion, and a commitment to excellence in patient care. These skilled healthcare professionals are pivotal in the operating room, ensuring patient comfort and safety during surgical procedures. Becoming a nurse anesthetist involves completing a rigorous educational journey, gaining hands-on clinical experience, obtaining certifications, and continuously staying updated with advancements in medical science.
While the challenges of being a nurse anesthetist are undeniable, the rewards are equally significant. The opportunity to make a tangible difference in patient’s lives, the high level of autonomy, and the competitive salary are just a few of the many gratifying aspects of this profession. The sense of fulfillment derived from contributing to the well-being of patients and the satisfaction of overcoming the demands of a high-stress environment makes being a nurse anesthetist a uniquely rewarding experience.
For those passionate about healthcare and wanting to provide specialized anesthesia care, the journey to becoming a nurse anesthetist presents an opportunity for a fulfilling and challenging career path. By embracing the challenges and rewards, nurse anesthetists can make a profound difference in patients’ lives and contribute to the advancement of anesthesia care for generations to come.
Nursing Articles
- ¿Cómo obtengo un título de fisioterapia en los EE. UU.?
- 10 Best Nursing Schools in Phoenix in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- 5 Reasons Why You Should Become a CNA
- 6 Nursing Scholarships For All Students
- About Us
- Accelerated Nursing Programs In Utah: Everything You Need To Know
- ADN vs BSN – What You Need to Know
- Advance Your Nursing Career Today!
- Amazing Texas College Responses to COVID-19
- APRN Salary Trends: What To Expect In The Coming Years
- Average Nurse Salary
- Becoming An HIV & AIDS Nurse
- Best 16 accelerated nursing programs in ny in 2023
- Best 22 LPN Programs in MA in 2023
- Best Accelerated BSN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in 2020 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in 2023: Explore Options Today
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Accelerated Nursing Programs in Massachusetts in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best ADN to MSN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Associate of Science in Nursing Degrees in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Degree Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Nursing Programs in Chicago in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Nursing Programs in Georgia in 2020 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Arizona in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in California in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Colorado in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in Connecticut in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in GA in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in Houston, Texas in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in Illinois in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Los Angeles in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Maryland in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Massachusetts in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN programs in Michigan in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in MN in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in New Jersey (NJ) in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in New York in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in North Carolina in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Ohio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Oklahoma in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Oregon in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best BSN Programs in PA in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in San Antonio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in San Diego in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Texas in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Utah in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Virginia in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN Programs in Washington in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best BSN to DNP Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best CNA Classes
- Best CNA Programs in the U.S. in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Community College Nursing Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best CRNA Schools in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best CRNA Schools in Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Direct Entry MSN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best DNP Degree Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best DNP Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best FNP Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Forensic Nursing Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Gifts for Nurses
- Best Healthcare Administration Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN Programs in Connecticut in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN to BSN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN to RN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LPN/LVN to BSN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best LVN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Masters Degree in Nursing Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Medical Assistant Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Medical Billing Schools
- Best MSN Degree Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best MSN Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2023: Explore Options Today
- Best Nursing Careers: 50 Different Types of Nurses
- Best Nursing Degree Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Informatics Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Programs in Athens, Georgia in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Programs in Indianapolis in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing School in Broward in 2023
- Best Nursing School in Fort Lauderdale in 2023 (On-Campus or Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in 2023: Explore Your Options Today
- Best Nursing Schools in Alabama in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Alaska in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Albany, NY in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Albuquerque, NM in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Arizona in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Arkansas in 2020 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Arlington Texas in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Atlanta in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Augusta, GA in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Austin, Texas in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Baltimore in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Baton Rouge in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Birmingham AL in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Boca Raton in 2023
- Best Nursing Schools in Boston in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Brooklyn, NY in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in California in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Central Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Charlotte, NC in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Chicago in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Cincinnati, OH in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Cleveland, Ohio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Colorado in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Colorado Springs in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Columbia, SC in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Columbus Ohio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Connecticut in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in D.C. in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Dallas in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Dayton, Ohio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Delaware in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Denver Colorado in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Des Moines in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in El Paso, TX in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Fayetteville, NC in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Fort Myers in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Fort Worth, Texas in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Georgia in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Greenville SC in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Greenville, SC in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Hawaii in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Houston in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Idaho in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Illinois in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Indiana in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Iowa in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Jacksonville FL in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Kansas City in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Kansas in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Kentucky in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Lancaster, PA in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Las Vegas in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Long Island, NY in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Los Angeles in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Louisiana in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Louisville, KY in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Maine in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Manhattan in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Maryland in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Massachusetts in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Memphis TN in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Miami in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Michigan in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Milwaukee in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Minneapolis in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Minnesota in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Mississippi in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Missouri in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Montana in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Montgomery, Alabama in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Nashville TN in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Nebraska in 2023 (On-Campus and Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Nevada in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New England in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Hampshire in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Jersey in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Mexico in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New Orleans in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in New York in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools In North Carolina in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in North Dakota in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Northern California in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in NYC in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Oahu in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Ohio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Oklahoma City in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Oklahoma in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Orange County in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools In Oregon in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Orlando Florida in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Pennsylvania in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Philadelphia in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Pittsburgh in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Portland, Oregon in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Queens in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Raleigh, NC in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Rhode Island in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Richmond VA in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Sacramento, CA in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Salt Lake City in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in San Antonio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in San Diego in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Savannah, GA in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Seattle WA in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in South Carolina in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in South Dakota in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in South Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Southern California in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Springfield, MO in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in St Louis, MO in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Tampa, Florida in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Tennessee in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Texas in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in the Bronx in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in the Midwest in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in the South in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Toledo, Ohio in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Utah in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Vermont in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Virginia Beach in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Virginia in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Washington in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in West Palm Beach FL in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in West Virginia in 2023 (On-Campus & Online)
- Best Nursing Schools in Wisconsin in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Nursing Schools in Wyoming in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Online Nursing Programs in 2023: Explore Your Options Today
- Best Online RN to BSN Programs in 2023
- Best Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Phlebotomy Certification Programs in the U.S. in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Physician Assistant Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in 2020: The Complete List (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in California in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in Florida in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in Nebraska (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in North Carolina in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in NY in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to BSN Programs in Texas in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best RN to MSN Online Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- Best Second Degree Nursing Programs in 2023 (Online & On-Campus)
- BSN vs. MSN Guide: Which One is Better for You?
- Building a Bright Future: Exploring the Best Nursing Schools in Texas
- Cardiac Nurse Salary in 2023
- Charge Nurse vs. Nurse Manager: What’s the Difference?
- CNA Meaning – How To Become A Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA)?
- CNA Requirements and Career Outlook
- CNA Salary in 2023
- College Planning for Deaf and Hard of Hearing Students
- College Resources for Students With Disabilities
- College Responses to COVID 19 in Kentucky
- College Responses to COVID 19 in South Dakota
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Iowa
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Maine
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Minnesota
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Rhode Island
- Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Vermont
- Colleges Responses to COVID-19 in Wisconsin
- Colleges’ Responses to COVID 19 in Nebraska
- Colleges’ Responses to COVID 19 in New Mexico
- Community Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Alabama
- Community Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Connecticut
- Community Colleges Responses to COVID 19 in Hawaii
- Cómo convertirse en fisioterapeuta [Guía definitiva]
- Compact Nursing States List
- Critical Care Nursing Salary
- Dialysis Nurse Salary in 2023
- DNP Salary in 2023
- DNP vs. NP: What’s the Difference?
- Elevate Your Medical Career: Ultrasound Tech Program Near Me
- Emergency Room Nurse Salary in 2023
- Empower Your Career: Discover The Best Nurse Practitioner Programs
- Exploring the Aesthetic Nurse Salary: How Much Do Aesthetic Nurses Earn
- Exploring the Earnings: Associate Degree in Nursing Salary Insights
- Exploring The Forensic Nurse Salary: How Much Do Forensic Nurses Earn
- Find a Healthcare Program
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes
- Find CNA Classes Here
- Find CNA Classes Near You
- Find CNA Classes Near You
- Find CNA Programs Near You
- Find Direct Entry MSN Programs
- Find Home Health Aide Classes
- Find LVN/LPN Classes
- Find Medical Assistant Classes
- Find Medical Assistant Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes
- Find Medical Billing and Coding Classes Near You
- Find Pharmacy Technician Classes Now
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes
- Find Phlebotomy Classes Near You
- Find Phlebotomy Classes Near You
- Find Phlebotomy Classes Near You
- Find the Best Medical Billing And Coding Classes
- Find the Best Nursing Programs
- Flight Nurse Salary in 2023
- FNP Salary Revealed: Your Path To Lucrative Earnings
- FNP vs. ACNP in 2023
- FNP-BC vs. FNP-C: Learn the Difference Between These Nurse Practitioner Certifications
- Guide to Financial Aid
- Guiding The Heart: Ethical Principles In Nursing Practice
- Healthcare Champions In The Classroom: Exploring School Nurses Salary Trends
- Highest Paying Nursing Careers in 2023
- Highest Paying Telehealth Nursing Jobs
- Home health care Nurse in 2023
- Hospice Nurse Salary Trends And Outlook: What To Expect
- How Long Is Nursing School?
- How Much Do Nurses Make?
- How Much Do Travel Nurses Make?
- How Much Does A Nurse Practitioner Make?
- How Much Does A Travel Nurse Make
- How Much Does Nursing School Cost
- How to Become a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
- How to Become a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
- How to Become a CNA
- How to Become a CRNA in 2023
- How To Become A Dermatology Nurse
- How to Become a Flight Nurse
- How To Become A Hospice Nurse
- How to Become a Legal Nurse Consultant (LNC)
- How To Become A Licensed Practical Nurse?
- How To Become A Medical Assistant in 2023
- How to Become a Military Nurse
- How To Become A Neonatal Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a NICU Nurse in 2023
- How To Become A Nurse Administrator
- How to Become a Nurse Anesthetist?
- How To Become A Nurse Esthetician
- How To Become A Nurse Informaticist
- How to Become a Nurse Manager
- How to Become a Nurse-Midwife
- How To Become A Phlebotomist
- How To Become A Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner
- How to Become a Registered Nurse (RN)
- How to Become a Registered Nurse First Assistant (RNFA)
- How To Become a Surgical Nurse in 2023
- How To Become A Telemetry Nurse: Steps, Salary, Career Opportunities
- How To Become A Trauma Nurse
- How to Become A Travel Nurse in 2023
- How to Become An Acute Care Nurse Practitioner (ACNP)
- How to Become an Aesthetic/Cosmetic Nurse
- How to Become an ER Nurse in 2023
- How to Become an ICU Nurse?
- How To Become An LPN
- How To Become An Obstetrics Nurse
- How To Become An Oncology Nurse
- How To Become An Operating Room Nurse
- How To Get Your Registered Nursing License in California
- How to Go From RN to MSN?
- How To Read An Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG)
- ICU Nurse Salary
- Illinois College Responses to COVID-19
- Inspiring Arizona college responses to COVID-19
- Interview with Brianna Taquinto
- Interview with Katelyn H
- Is A Surgical Nursing Career Right For You?
- Is Nursing School Really As Hard As Everyone Says?
- Labor And Delivery Nurse Salary Guide In 2023
- Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN)
- List of the Best Nursing Schools in Houston in 2023
- Looking for Nursing Classes Near You or Online?
- Looking for Online Nursing Programs?
- LPN Certificates vs Nursing Associate Degrees
- LPN Salary in 2023
- LPN To RN Program : Bridge Your Nursing Career
- LPN vs. RN Guide: Which One is Better for You?
- Massachusetts College Responses to COVID-19
- Mastering The Art Of Writing A Nursing Care Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
- Medical Assistant Salary in 2023
- Medical Assistant vs CNA
- Mental Health Nurse in 2023
- Missouri College Responses to COVID-19
- MSN vs. DNP Guide: Which One Is Better for You?
- Multistep
- NCLEX Lab Values Nursing Students Need To Know
- Neonatal Nurse salary in 2023
- NICU Nursing: What Every Nurse Needs to Know
- Non Clinical Nursing Jobs in 2023
- Normal Lab Values Every Nurse Should Know
- North Carolina Community College Responses to COVID-19
- Nurse Administrator Salary in 2023
- Nurse Anesthetist Salary in 2023
- Nurse Anesthetist Schooling: Your Path to Becoming a Certified CRNA
- Nurse Educator Salary in 2023
- Nurse Practitioner (NP) vs Physician Assistant (PA): Which Role is Right for You?
- Nurse Practitioner Salary in 2023
- Nurse Practitioner Salary in 2023
- Nursing Certifications in 2023
- Nursing Informatics Salary Guide
- Nursing Informatics Salary in 2023
- Nursing Requirements
- Nursing Schools in Reno NV
- Nursing Specialties in 2023
- OB-GYN Nurse Salary in 2023
- Ohio College Responses to COVID-19
- Oncology Nurse Salary in 2023
- Oregon College Responses to COVID-19
- Pediatric Nurse Salary and Career Guide: All You Need to Know
- Perioperative Nurse Salary in 2023
- Plastic Surgery Nurse Salary in 2023
- Privacy Policy
- Pros And Cons Of Being A Night Shift Nurse
- Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner Salary
- Psychiatric Nurse Salary
- Ranking Methodology
- Registered Nurse (RN) vs. Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN)
- Registered Nurse Salary in 2023
- RN Case Manager Salary in 2021
- RN Programs – Start Your Journey As A Registered Nurse
- RN to BSN Nursing Programs in PA
- RN to BSN Program Scholarship
- RN to BSN Programs in Iowa
- RN to BSN Programs in Missouri
- RN to MD: Everything You Need to Know
- Student Loan Forgiveness for Nurses in 2023
- Student Loan Forgiveness Programs For Nurses
- Terms of Service
- Thank You
- The Average Practice Nurse Salary: A Comprehensive Guide
- The Complete List of Common Nursing Certifications
- The Difference Between Nurse Practitioner and Physician Assistant
- The Different Nursing Levels Explained
- The Essential Skills And Qualifications To Become A Postpartum Nurse
- The Ultimate Guide to Nursing Diagnosis in 2023
- Top Paying Careers for MSN Nurses
- Trauma Nurse Salary in 2023
- Travel Nurse Salary in 2023
- Travel Nursing 101: Everything You Need To Know
- Types Of Masters Degrees In Nursing
- Types of Nursing Degrees
- Types of Nursing Specialties
- Unlocking the Potential: Advancing Your Dialysis Nurse Career
- Unraveling The Difference Between Physician Assistant And Nurse Practitioner
- Visionaries of Beauty: Discovering the Best Aesthetic Nurse Jobs
- What Are The Prerequisites For Nursing School?
- What Are The Pros And Cons Of Joining A Nurse Union?
- What Can You Do With a Nursing Degree in 2023
- What Does A CNA Do?
- What Does a Midwife Salary Look Like?
- What Does A Nurse Practitioner Do-Role And Responsibilities:
- What is a BSN Degree?
- What is a Cardiac Nurse?
- What is a Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)?
- What is a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA)?
- What is a Charge Nurse?
- What is a Clinical Nurse Specialist?
- What is a CNA (Certified Nursing Assistant)
- What Is A DNP Degree?
- What is a DNP in 2023
- What is a Family Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a Home Health Nurse?
- What is a Hospice Nurse? | Everything You Need to Know
- What is a Labor and Delivery Nurse? | Everything You Need to Know
- What Is A Legal Nurse Consultant?
- What is a Military Nurse?
- What is a Neonatal Nurse?
- What Is A Night Shift Nurse?
- What is a Nurse Case Manager?
- What is a Nurse Practitioner in 2021
- What is a Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a PACU Nurse?
- What is a Pediatric Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a Pediatric Nurse?
- What is a Physician Assistant?
- What is a Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner?
- What is a Psychiatric Nurse?
- What is a Public Health Nurse
- What is a Registered Nurse (RN)?
- What is a Registered Nurse First Assistant (RNFA)?
- What is a School Nurse? | All You Need to Know
- What is a Trauma Nurse?
- What is a Traveling Nurse?
- What is a Wound Care Nurse?
- What is an ADN? Associate Degree in Nursing Programs
- What Is an Advanced Practice Nurse
- What is an Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN)?
- What Is An APRN? Understanding The Role Of An APRN
- What is an ER Nurse?
- What is an OB Nurse?
- What is an Oncology Nurse?
- What is Critical Care Nursing?
- What is Forensic Nursing?
- What Is Holistic Nursing in 2023
- What is Neonatal Nurse in 2023
- What is Nursing Informatics in 2023
- What is Nursing Informatics?
- What is Perioperative Nursing?
- What Is Psychiatric Nurse Practitioner in 2023
- What Is the difference between a CNA and an LPN?
- What is the Difference Between an LPN and RN?
- What Is the Difference Between RN and BSN Degrees?
- What is the TEAS Exam and How to Prepare For It?
- What to Expect in Nursing School Clinicals
